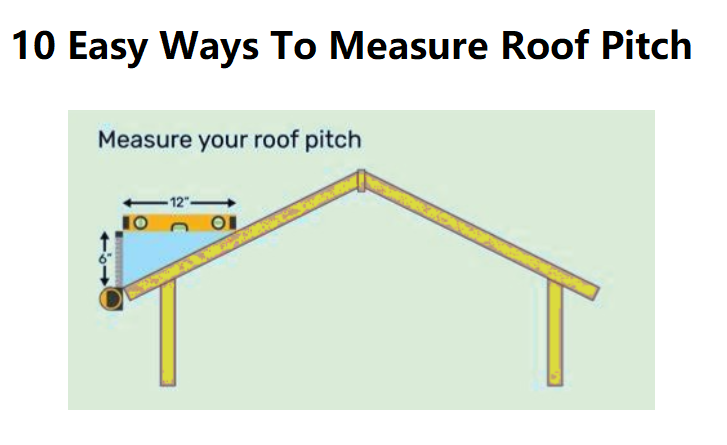
1. Use a Carpenter’s Level and a Tape Measure
This traditional method is widely used for its simplicity and accuracy. Here’s how:
- Place a carpenter’s level flat on the roof surface.
- Measure 12 inches horizontally along the level (run).
- From the end of the 12-inch mark, measure vertically down to the roof’s surface (rise).
The pitch is expressed as a ratio of rise to run. For example, a 6-inch rise over a 12-inch run is a 6:12 pitch.
2. Use a Smartphone App
Modern technology makes it even easier to measure roof pitch. Several apps are available to help, such as:
- Angle Finder Apps: Use your smartphone’s built-in gyroscope to measure angles.
- Roof Pitch Calculators: Input the rise and run, and these apps will calculate the pitch for you.
Follow the app’s instructions for quick and accurate results.
3. Try a Roof Pitch Gauge
A roof pitch gauge is specifically designed for this purpose. It’s simple to use:
- Place the gauge on the roof surface.
- Adjust the movable arm to align with the roof slope.
- Read the pitch value on the scale.
This tool is inexpensive and available at most hardware stores.
4. Use a Protractor and String
This low-tech method is surprisingly effective:
- Attach a weight to one end of a string to act as a plumb line.
- Hold a protractor flat against the roof surface.
- Allow the string to hang freely and note where it intersects with the protractor scale.
Use a pitch conversion chart to translate the angle into a pitch ratio.
5. Measure from Inside the Attic
If accessing the roof is unsafe, measure pitch from the attic:
- Place a straightedge horizontally along the underside of a rafter.
- Measure 12 inches horizontally (run) and vertically to the rafter (rise).
This method avoids the need to climb onto the roof.
6. Use a Framing Square
A framing square is a classic tool for measuring roof pitch. Here’s how:
- Place the framing square on the roof surface.
- Align one side with the run (e.g., 12 inches).
- Measure the rise where the roof intersects with the vertical side of the square.
This method is straightforward and highly accurate.
7. Employ a Digital Angle Finder
For precision, a digital angle finder is an excellent choice:
- Position the device directly on the roof surface.
- Read the angle on the digital display.
Many digital angle finders also provide direct pitch conversions.
8. Use a Laser Level
A laser level offers a non-contact way to measure pitch:
- Set up the laser level to project a horizontal line.
- Measure the vertical rise from the roof to the laser line and the horizontal run.
This method is ideal for steep roofs or inaccessible areas.
9. Calculate from Blueprints
If you have architectural plans, you can calculate roof pitch directly:
- Locate the roof’s section on the blueprint.
- Measure the rise and run dimensions from the drawing.
Divide the rise by the run to determine the pitch ratio.
10. Estimate with Visual Cues
For quick approximations, use visual cues:
- Low Pitch: Appears almost flat (3:12 or less).
- Moderate Pitch: Clearly sloped (4:12 to 6:12).
- Steep Pitch: Very steep (7:12 or more).
This method is best for rough estimates and visual assessments.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back